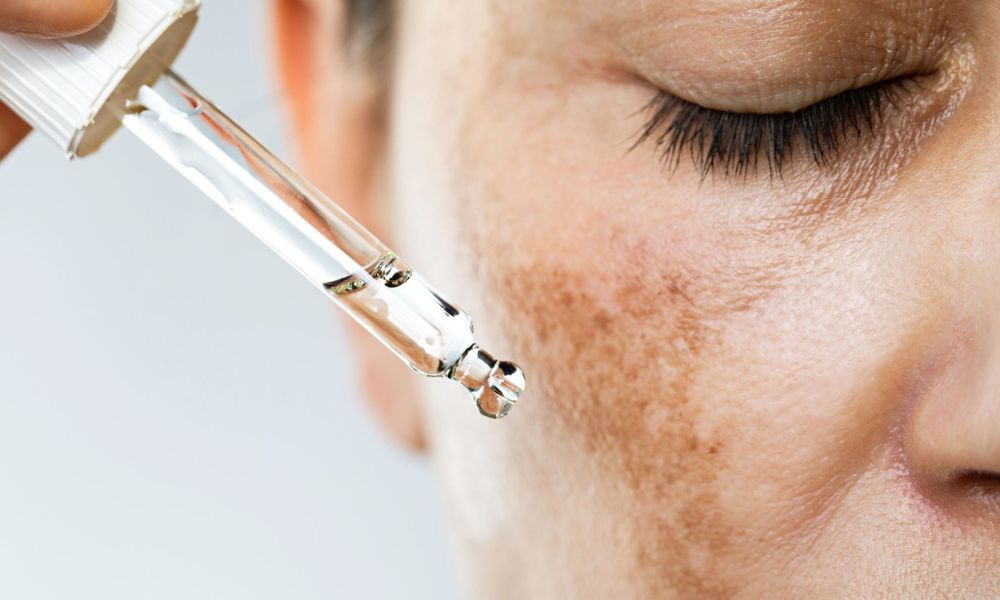
Hyperpigmentation refers to dark patches on the skin caused by excessive melanin production. It can result from factors such as acne scars, sun exposure, or hormonal changes. Fortunately, multiple treatment options can help reduce its appearance. Here are a few proven strategies for optimal results.
1. Face Acids
Face acids, also known as skin acids, promote exfoliation by removing the top layer of the skin. This process encourages the formation of new skin cells, leading to a more even complexion and smoother texture. For added skin brightening and rejuvenation, consider incorporating a Glutathione Injection into your skincare routine, which helps to lighten and enhance your skin’s overall appearance.
Common OTC options include:
- Alpha hydroxy acids (glycolic, lactic, citric, malic, tartaric acid)
- Azelaic acid
- Kojic acid
- Salicylic acid
- Vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid)
These acids are ideal for mild hyperpigmentation, especially for individuals with lighter skin tones. It is recommended to use products with 10% or lower acid content to minimize the risk of irritation.
2. Retinoids
Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, have a small molecular structure that allows deep penetration into the skin. Available in both OTC and prescription-strength formulations, retinoids help improve skin tone.
OTC retinoids are generally safe for all skin types, but people with darker skin should consult a dermatologist before long-term use. Although retinoids are primarily used for treating wrinkles, they may also assist with hyperpigmentation.
Example Product: Differin Gel, which addresses both acne and pigmentation concerns.
3. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels utilize stronger acid concentrations to exfoliate the skin, reducing pigmentation by removing the epidermis and, in some cases, penetrating deeper layers. Professional chemical peels offer quicker results but may also carry risks such as redness, irritation, or scarring. Sunscreen application is crucial after a peel since the skin becomes highly sensitive to UV rays.
Best for: Age spots, sun damage, melasma, and uneven skin tone. Fairer skin tones may see faster results.
4. Laser Peel (Skin Resurfacing)
Laser treatments use concentrated light beams to reduce pigmentation. They are classified into two types:
- Ablative Lasers: Remove layers of skin for dramatic results.
- Non-ablative Lasers: Stimulate collagen growth while tightening the skin.
Ablative lasers work better for fair skin tones, while non-ablative lasers may sometimes darken the skin instead of lightening it.
5. Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy
IPL therapy, or photo facial, is a non-ablative laser treatment that stimulates collagen production, improving overall skin tone. It is effective for flat pigmentation spots and is most suitable for lighter skin tones.
6. Microdermabrasion
This procedure removes only the epidermis, making it ideal for treating superficial pigmentation. Several sessions might be required to see visible results. It is best suited for individuals with fair skin.
7. Dermabrasion
Unlike microdermabrasion, dermabrasion extends into the dermis, addressing deeper pigmentation issues like acne scars and sun damage. While it is effective, it carries a risk of post-treatment hyperpigmentation.
8. Lightening Creams
Available in both OTC and prescription forms, these creams gradually lighten pigmentation with ingredients such as hydroquinone and vitamin C. They are applied once or twice daily for consistent results.