In today’s rapidly evolving world, the conversation around health equity and access to care has never been more pertinent. As healthcare systems strive to accommodate a diverse range of needs, the focus on ensuring equitable access to quality care becomes increasingly crucial. This article delves into why health equity matters, the barriers that undermine it, and how improving access to care can lead to better health outcomes for all.
Understanding Health Equity
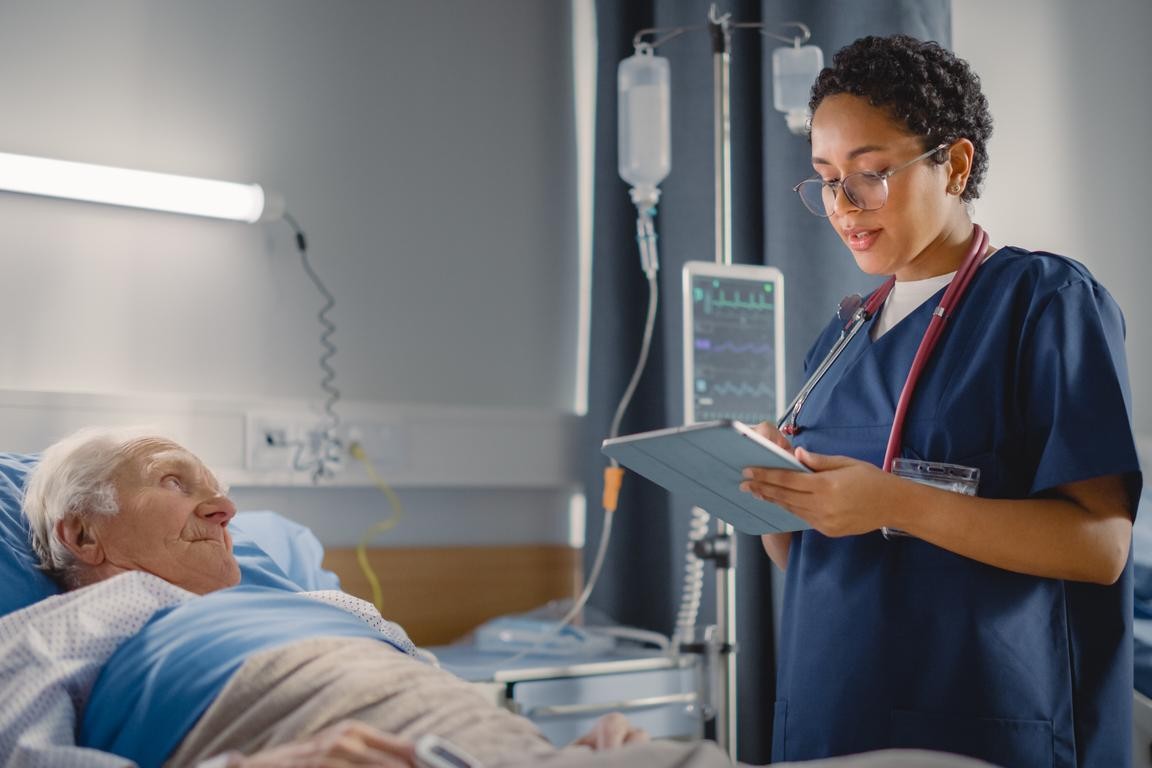
Health equity refers to the principle of fairness in health care, ensuring that all individuals have the opportunity to attain their highest level of health, regardless of their socioeconomic status, race, gender, or geographical location. Unlike equality, which implies treating everyone the same, equity involves addressing the systemic disparities that prevent certain groups from receiving the same level of care and opportunities.
Health disparities arise from various factors including socioeconomic status, education, race, and geographical location. These disparities often result in unequal access to quality health care, leading to significant differences in health outcomes. Health equity aims to reduce these disparities and ensure that everyone has the resources and support needed to achieve optimal health with the help of troy orthodontist.
The Significance of Health Equity
- Improved Health Outcomes: Ensuring equitable access to care leads to better health outcomes across all populations. When individuals receive timely and appropriate medical attention, it reduces the incidence and severity of diseases, resulting in a healthier overall society.
- Economic Benefits: Investing in health equity can also yield significant economic benefits. A healthier population is more productive, which contributes to economic growth. Reducing health disparities can lower healthcare costs by preventing chronic conditions and minimizing emergency care needs.
- Social Justice: Health equity is a matter of social justice. Everyone deserves the right to quality health care, and addressing inequities aligns with broader efforts to promote fairness and equality in society.
- Strengthening Healthcare Systems: Focusing on health equity can lead to improvements in healthcare systems. Addressing the unique needs of underserved populations often drives innovations in care delivery and enhances the overall effectiveness of the healthcare system.
Barriers to Health Equity and Access to Care
Despite the importance of health equity, numerous barriers hinder access to care and perpetuate health disparities. These include:
- Economic Barriers: The cost of healthcare services can be prohibitive for low-income individuals and families. High medical costs, lack of insurance coverage, and financial instability contribute to delayed or forgone care.
- Geographical Barriers: Rural and underserved areas often lack sufficient healthcare facilities and professionals. Residents in these regions may face long travel distances to access care, which can deter them from seeking medical attention.
- Cultural and Linguistic Barriers: Language differences and cultural misunderstandings can create obstacles to effective communication between patients and healthcare providers. This can result in misdiagnoses, inadequate treatment, and reduced patient satisfaction.
- Educational Barriers: Health literacy plays a crucial role in how individuals manage their health. Those with lower levels of education may struggle to understand medical information and navigate the healthcare system effectively.
- Systemic Discrimination: Discrimination based on race, gender, or socioeconomic status can affect the quality of care received. Systemic biases in healthcare can lead to disparities in treatment and health outcomes.
Strategies to Promote Health Equity and Access to Care
Addressing health equity and improving access to care require a multifaceted approach. Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Expanding Coverage: Expanding health insurance coverage through public programs and subsidies can help reduce financial barriers to care. Ensuring that everyone has access to affordable insurance options is crucial for achieving health equity.
- Increasing Healthcare Access in Underserved Areas: Investing in healthcare infrastructure and resources in rural and underserved communities can help bridge the access gap. Mobile clinics, telemedicine, and community health centers can provide essential services to these populations.
- Cultural Competency Training: Healthcare providers should receive training in cultural competency to better understand and address the needs of diverse patient populations. This includes learning about different cultural practices, beliefs, and communication styles.
- Enhancing Health Literacy: Improving health literacy through education and outreach programs can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health. This includes providing clear, accessible information and resources to help people navigate the healthcare system.
- Addressing Systemic Biases: Healthcare systems must actively work to identify and address systemic biases and discriminatory practices. Implementing policies that promote fairness and inclusivity can help ensure that all patients receive equitable treatment.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with communities to understand their specific needs and preferences can lead to more effective and culturally appropriate health interventions. Collaboration with local organizations and stakeholders is essential for tailoring solutions to diverse populations.
The Role of Policy and Advocacy
Policymakers and advocates play a critical role in advancing health equity. Effective health policies can address systemic barriers and promote fair access to care. Advocacy efforts can raise awareness about health disparities and push for necessary changes in healthcare policies and practices.
Key areas for policy focus include:
- Affordable Care Act (ACA) Expansion: Supporting and expanding ACA provisions can help increase insurance coverage and reduce disparities in access to care.
- Medicaid Expansion: Advocating for the expansion of Medicaid in states where it has not been adopted can improve access to care for low-income individuals.
- Healthcare Workforce Diversity: Promoting diversity within the healthcare workforce can help improve cultural competency and address disparities in care.
- Social Determinants of Health: Addressing social determinants such as housing, education, and employment can have a significant impact on health outcomes and equity.
Conclusion
Health equity and access to care are fundamental to creating a just and effective healthcare system. By addressing the barriers that contribute to health disparities and implementing strategies to promote fairness, we can work towards a healthier society where everyone has the opportunity to thrive. Whether through policy changes, community engagement, or individual actions, advancing health equity requires a collective effort to ensure that all people, regardless of their background or circumstances, can achieve their highest level of health