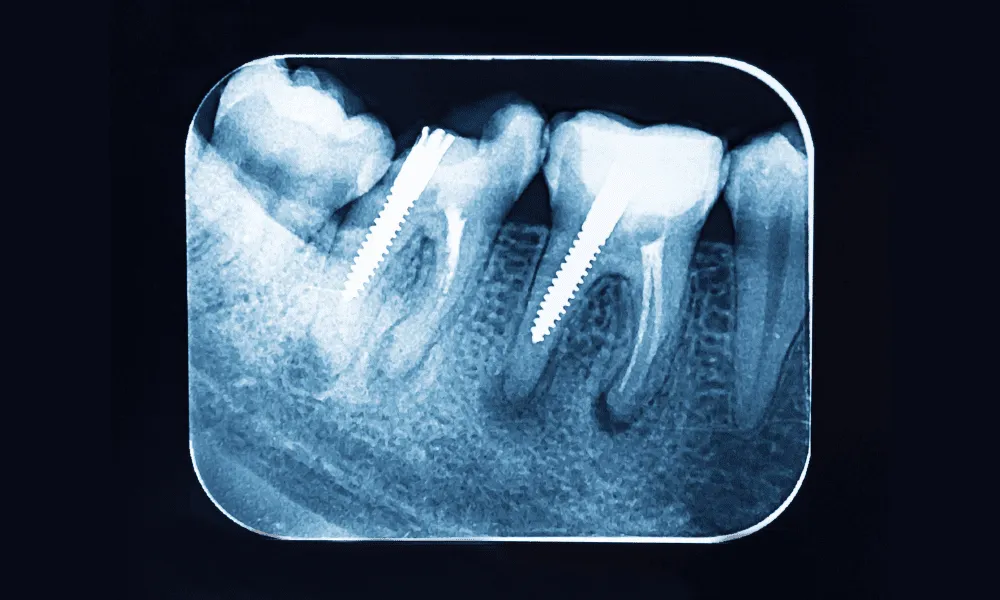
Dental X-rays are essential in pediatric dental care by revealing important information that cannot be detected during a visual examination alone. These diagnostic images help dentists monitor oral development, identify hidden problems, and guide treatment decisions for children. Smile Buds Pediatric Dentistry & Orthodontics provides various dental X-rays for comprehensive pediatric dental care.
Common types of dental X-rays for children
Several specialised X-ray techniques are used in pediatric dentistry, each serving specific diagnostic purposes:
- Bitewing X-rays capture both upper and lower jaw crown images simultaneously. These images excel at detecting cavities between teeth and checking the fit of dental restorations. They also help evaluate bone levels around teeth, essential for monitoring periodontal health. Most children receive bitewing X-rays once yearly, though frequency varies based on individual cavity risk.
- Periapical X-rays show the entire tooth from crown to root tip, including surrounding bone structure. These detailed images help diagnose problems affecting tooth roots and surrounding bone tissue and detect abscesses or cysts. They’re typically taken when a child experiences specific symptoms like pain or swelling or following dental trauma.
- Panoramic X-rays give a view of the entire mouth in a single image. This wide-angle view shows all teeth, jaws, temporomandibular joints, and sinuses. Panoramic images help assess tooth development, identify impacted teeth, evaluate growth patterns, and screen for abnormalities. Most children have their first panoramic X-ray around age 6-7 when permanent teeth begin emerging.
- Cephalometric X-rays capture the side profile of a child’s head, highlighting relationships between teeth, jaws, and facial bones. These specialised images primarily support orthodontic evaluation and treatment planning by assessing growth patterns and jaw relationships.
How X-rays guide diagnosis and treatment?
Dental X-rays reveal information critical to children’s oral health that cannot be seen during clinical examination:
- Between teeth: Even the most thorough visual inspection cannot detect early decay in these spaces. X-rays can identify cavities in their earliest stages when intervention is more straightforward and less invasive.
- Beneath the gum line: X-rays show developing permanent teeth, helping dentists monitor their position and formation. This information allows for timely intervention if issues with eruption patterns or tooth development are detected.
- Inside teeth and bone: X-rays reveal infections, cysts, or abnormalities that might remain undetected until they cause symptoms or visible changes. Early detection of these problems prevents unnecessary pain and complications.
- For growth assessment: Certain X-rays track jaw development and space available for emerging permanent teeth. This information helps determine if interventions like space maintainers are needed following the premature loss of baby teeth.
Integrating X-ray findings with clinical examination provides a comprehensive picture of a child’s oral health, guiding preventive strategies and necessary treatments.
When dental X-rays are recommended?
The decision to take dental X-rays depends on multiple factors rather than a fixed schedule:
- Age and developmental stage significantly influence X-ray needs. Children with primary teeth typically require fewer X-rays than those with mixed or permanent dentition. Many children have their first X-rays around age 5-6, coinciding with the eruption of permanent teeth.
- Cavity risk assessment affects X-ray frequency. Children with higher risk factors for decay, such as previous cavities, deep grooves in teeth, or specific dietary habits, may need more frequent monitoring.
- Growth monitoring requires periodic panoramic or cephalometric X-rays during key developmental periods, particularly for children who might need orthodontic intervention. These comprehensive images track jaw growth and tooth eruption patterns.
- Symptoms or clinical findings such as pain, swelling, trauma, or visual anomalies often indicate the need for specific X-rays to diagnose underlying issues. These targeted images help determine appropriate treatment approaches.
Dental professionals carefully weigh the benefits of diagnostic information against radiation considerations to provide appropriate, individualised care for young patients.
Name: Smile Buds Pediatric Dentistry & Orthodontics
Address: 3342 Verdugo Rd suite b, Los Angeles, CA 90065
Website: https://www.smilebuds.com/
Phone: (323) 825-8558